The role of knowledge brokers in advancing climate action
The role of knowledge brokers in advancing climate action
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has called for systems-wide transitions, resilience building and an urgent all-of-society response to address the climate change crisis. While research information and its tailoring into accessible knowledge products plays an important role in informing climate decision-making and action, strong knowledge and innovation brokering are also essential to navigate a complex environment that encompasses a range of sectors and stakeholders with different values and priorities, at multiple scales.
What is knowledge brokering?
Knowledge brokering is the process of moving knowledge into action, where knowledge brokers link producers and users of knowledge to facilitate the generation, dissemination and eventual use of that knowledge (from Bielak et al, 2008). The range of activities they are involved in can be understood along a spectrum that goes from working with information flows to seeking to bring about systemic change (see figure below).
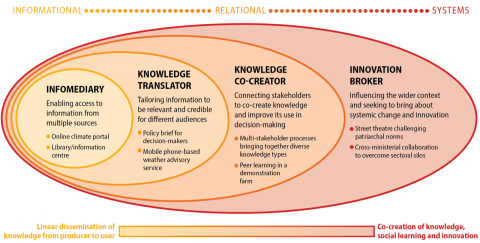
Whose knowledge are we referring to?
A critical role of knowledge brokers is to bring different knowledge holders and knowledge types together. These could include western scientific knowledge generally provided by academic researchers, but also experiential, applied knowledge normally held by practitioners, technical officers or those working in the field. Furthermore, traditional, often tacit knowledge that is owned by Indigenous communities or other local stakeholders is critical for sustainable and equitable action on the ground. Creating inclusive, safe spaces for these various knowledge holders to come together in a way that respects the value and validity of each, is essential for successful knowledge brokering.
What are climate knowledge brokers being called to do?
Although producing relevant, credible evidence is critical, it is usually insufficient on its own to foster shifts in policy and action – especially for a complex problem like climate change.
Such evidence must be accompanied by activities that assist decision-makers to understand the value of the knowledge and how it can be applied to their context. Whilst knowledge brokers have often focused on making knowledge more relevant and accessible (the left-hand side of the spectrum), the scale and urgency of the climate crisis today calls for knowledge brokering practice to move towards innovation brokering (on the right side of the spectrum).
In the context of the urgent climate crisis, climate knowledge brokers need to increasingly see their role as:
A facilitator of change seeking to strengthen relationships, networks and understanding on the climate challenge, based on diverse types of knowledge and experience, to ensure appropriate decisions are taken and implemented for a more climate-resilient world.
Download the CDKN Essentials here.
Download the additional journal article titled: Effective climate knowledge brokering in a world of urgent transitions
For more information, visit the project page here


