Ecosystem-based Adaptation: Priority action area
Ecosystem-based Adaptation: Priority action area
Context
Given the interconnected challenges of biodiversity loss, inequality and climate change, EbA offers a holistic approach to adaptation that addresses these contemporary challenges and recognises the interconnectedness between ecosystems and human well-being.
Working Group II of the IPCC highlights the many interlinkages between people and nature, noting that EbA, as well as Nature-based Solutions (NbS) and Ecosystem-based Disaster Risk Reduction (Eco-DRR), can help strengthen the resilience of social and natural systems against climate change.
Several key policy processes and frameworks at international level guide the implementation of EbA approaches including those linked to the Rio Conventions: the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), as well as the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction and the Sustainable Development Goals.
At a national level, governments play a key part in developing policies, strategies and regulations that support EbA and align with international agreements – for example, the CBD and Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) both provide a framework for countries to develop and implement National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans.
CDKN aims to ensure EbA is also a core part of locally-led climate action and adaptation strategies. Ecosystems and natural resources are often subject to competing interests and resource conflicts, with marginalised communities bearing the brunt of environmental degradation and climate change impacts. With this in mind, a locally-led approach is key to ensuring that the needs of local communities and marginalised groups are recognised – their knowledge, experiences, rights and priorities must be central to adaptation planning and decision-making processes.
Promoting gender equality and social inclusion (GESI) in EbA interventions not only increases their effectiveness but also contributes to addressing underlying drivers of social-ecological vulnerability and inequality.
Objectives
Specific objectives of CDKN’s EbA work include:
- Mobilising knowledge and Southern-led leadership on transformative EbA;
- Strengthening capacities of actors and institutions for implementing transformative EbA through knowledge brokering approaches;
- Leveraging and supporting partnerships, funding and collaborations for scaling transformative EbA.
Activities
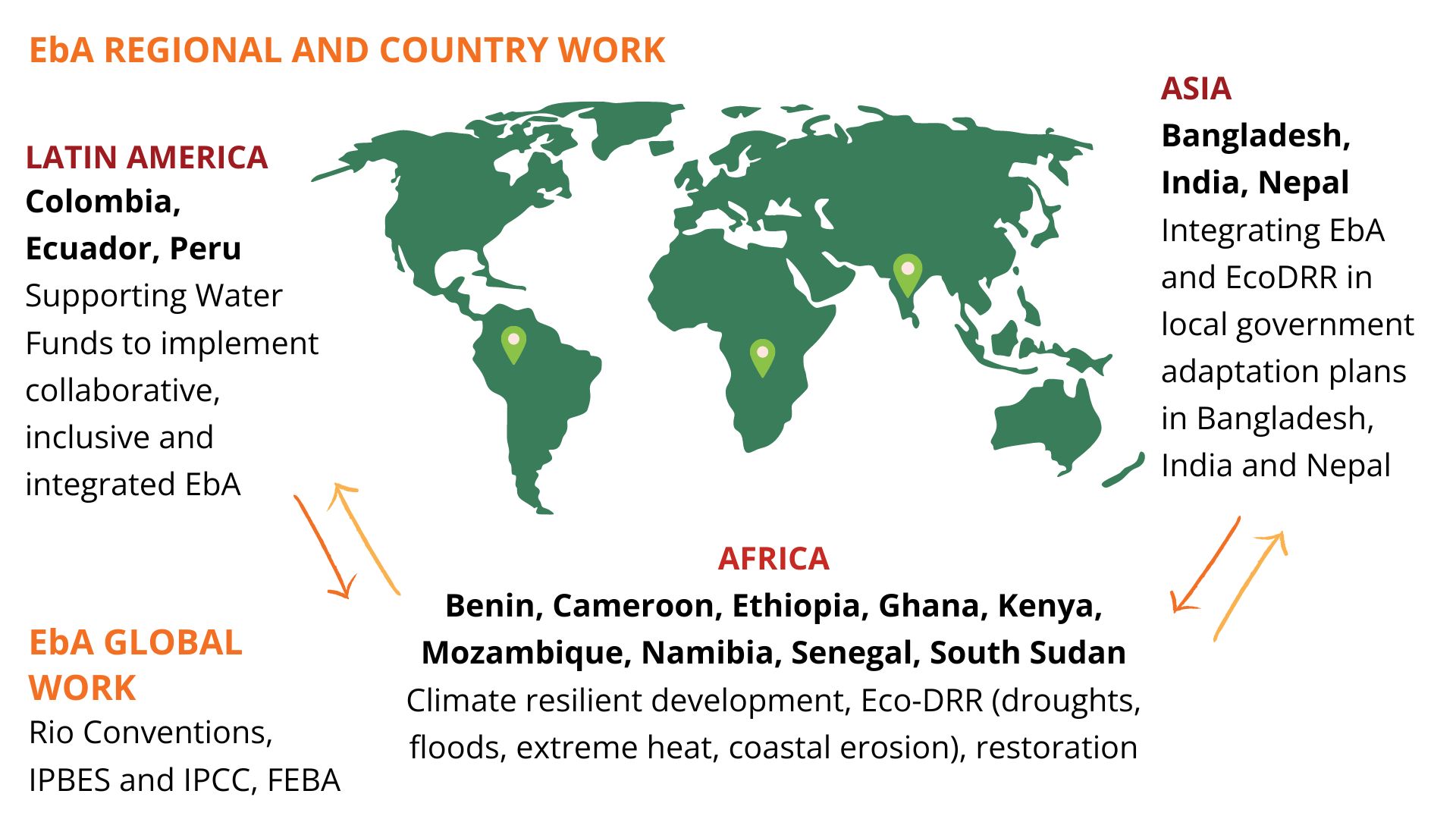
CDKN plays an active role in an international community of practice, Friends of Ecosystem-based Adaptation (FEBA), co-leading a working group on targets 8 and 11 of the GBF with the Secretariat of the CBD, and continues to engage in the FEBA EbA Knowledge Days and the ENACT initiative.
At global level, CDKN is involved in co-authoring chapters of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversty and Ecosytem Services (IPBES) Nexus Assessment and is engaging in related supporting activities of Capacity Development for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services Experts (CABES) and Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services Network (BesNet).
At a regional level, SouthSouthNorth recently became a charter member of the Global Landscapes Forum where CDKN, as a programme within SSN, has been actively involved in supporting GLF’s Youth in Landscapes Initiative, which aligns with CDKN’s sister project, Justice in a Changing Climate (CDKNJ).
Outputs
- Harnessing Ecosystem-based Adaptation to drive progress on implementing the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework: A publication launched at COP16 with FEBA, RARE, Convention on Biodiversity, GIZ, Bird Life International, UN-WMCM, Federal Ministry for Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, IKI, and IUCN that offers consolidated evidence, guidance and case studies on EbA to support the uptake of EbA across national strategies and plans for all three Rio Conventions and inform the development of revised national biodiversity and climate commitments.
Contact
For more information contact:
Nadia Sitas, CDKN EbA Lead on e-mail nadia@southsouthnorth.org or Linkedin






